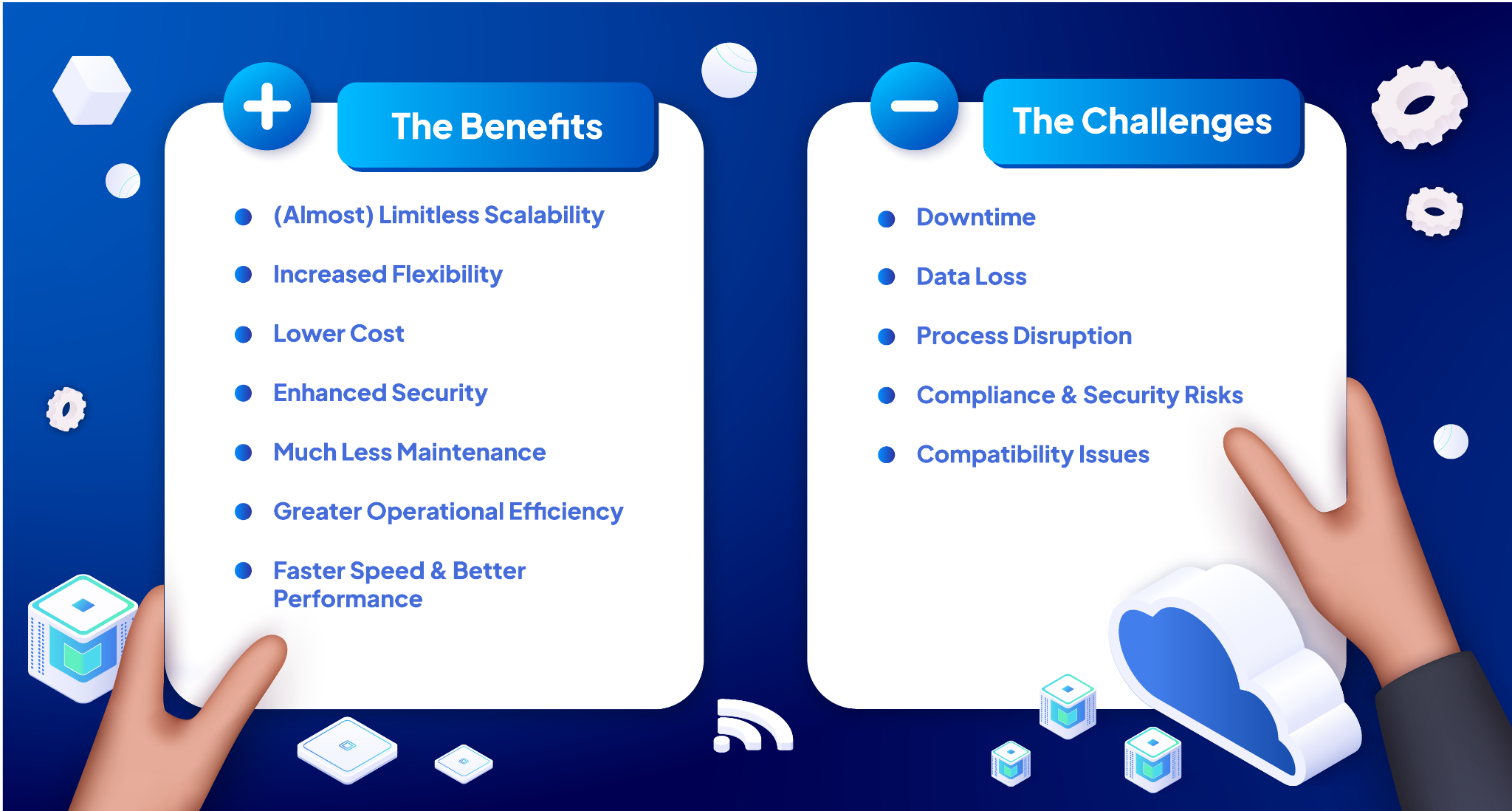
As businesses and organizations continue to embrace digital transformation, cloud computing has emerged as a key player in driving innovation, agility, and cost savings. Moving to the cloud offers a wide range of benefits, with cost reduction being one of the most compelling reasons why many businesses are making the shift. By migrating to cloud infrastructure, companies can reduce capital expenses, optimize operational costs, and take advantage of scalable solutions that align with their needs.
This article delves into the cost-saving advantages of migrating to the cloud and how organizations can benefit from this transition in both the short and long term.
What is Cloud Migration?
Before exploring the cost-saving advantages, it is essential to understand what cloud migration is. Cloud migration refers to the process of moving an organization’s data, applications, and IT infrastructure from on-premises systems to a cloud-based environment. This can involve migrating to public, private, or hybrid cloud platforms, depending on an organization’s specific needs and requirements.
There are various approaches to cloud migration, including:
- Lift and shift: Moving applications or data without making significant changes to the underlying code or architecture.
- Re-platforming: Making minor adjustments to optimize applications for the cloud.
- Re-architecting: Rebuilding or redesigning applications to leverage the full potential of cloud environments.
By migrating to the cloud, organizations can achieve cost savings in several critical areas.
Reducing Capital Expenses
Elimination of Physical Infrastructure Costs
One of the most significant cost-saving advantages of migrating to the cloud is the reduction in capital expenses associated with maintaining on-premises IT infrastructure. Traditionally, businesses needed to invest in expensive physical hardware, such as servers, storage devices, networking equipment, and data centers. Additionally, they were responsible for the ongoing maintenance, upgrades, and energy costs associated with these assets.
Cloud providers, on the other hand, offer businesses the ability to access infrastructure as a service (IaaS), allowing them to pay only for what they use. This means businesses can eliminate the upfront cost of purchasing and maintaining physical hardware and avoid the ongoing expenses of energy consumption and hardware updates.
With cloud computing, companies can access scalable infrastructure on demand, without the need to invest in physical equipment that may become obsolete or underutilized over time.
Avoiding Data Center Expenses
Maintaining an in-house data center can be expensive, requiring significant investments in facilities, cooling systems, power supply, and other supporting infrastructure. Migrating to the cloud can help organizations eliminate the costs associated with building and maintaining physical data centers. Cloud providers have vast data centers that they maintain, ensuring the infrastructure is always up-to-date and operational, reducing the burden on businesses to manage these resources themselves.
By using the cloud, organizations no longer need to worry about the costs of securing, staffing, and maintaining a physical data center. Instead, they pay for the services they use and avoid the complex logistics of managing data storage and network infrastructure.
Optimizing Operational Costs
Pay-as-You-Go Pricing Model
One of the most appealing aspects of cloud computing is its pay-as-you-go pricing model, which allows businesses to only pay for the resources they consume. This model is a significant cost-saving advantage over traditional IT infrastructure, where companies often overinvest in hardware to meet peak demand, leaving resources underutilized during periods of low activity.
The cloud’s flexibility enables businesses to scale resources up or down depending on their requirements, helping them optimize their spending. For instance, during times of high demand, businesses can temporarily scale up their cloud resources to accommodate traffic spikes and scale back down when demand decreases. This ensures that businesses are not paying for unnecessary resources, leading to greater cost efficiency.
Reduced IT Maintenance Costs
Cloud service providers take care of the maintenance and management of infrastructure, software, and services, including updates, security patches, and backups. This significantly reduces the need for businesses to employ a large IT team to manage and maintain these tasks in-house. IT departments can focus on more strategic initiatives rather than handling the day-to-day upkeep of hardware and software systems.
By outsourcing infrastructure management to the cloud provider, businesses can save on labor costs associated with maintaining systems, troubleshooting issues, and implementing updates. Moreover, cloud providers often have dedicated teams of experts, ensuring that the systems are always running optimally and securely.
Streamlined Software Licensing Costs
Cloud-based software, also known as Software as a Service (SaaS), offers businesses the opportunity to reduce the complexities and costs associated with traditional software licensing. Instead of purchasing perpetual licenses for each user or device, businesses can subscribe to cloud-based software and pay based on usage. This subscription-based model provides several benefits:
- Lower upfront costs: Instead of paying a large lump sum for software licenses, businesses can spread out the costs through a subscription-based pricing structure.
- Reduced license management overhead: SaaS providers handle license compliance, updates, and support, eliminating the need for businesses to track and manage multiple software licenses.
- Scalability: As the business grows, it can easily scale up the number of software licenses it needs, and it only pays for what it uses.
By migrating to cloud-based software, businesses can streamline their software expenses and reduce the costs associated with traditional software licensing.
Improving Efficiency and Productivity
Increased Collaboration and Remote Work
Cloud-based collaboration tools, such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, and Slack, provide employees with the ability to work together from anywhere with an internet connection. This increased flexibility leads to higher productivity and more efficient teamwork. Employees can access documents, share information, and communicate seamlessly without being tied to a specific office location.
In addition, the ability to collaborate in real time means that businesses can expedite decision-making processes and reduce downtime. This boost in productivity can translate into cost savings by improving overall operational efficiency and reducing time spent on manual tasks or delays.
Automation and AI Integration
Cloud platforms often come with integrated tools that enable businesses to automate repetitive tasks and integrate artificial intelligence (AI) into their operations. These technologies can streamline workflows, reduce human error, and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities.
For example, cloud-based AI tools can automate data analysis, customer service responses, and other routine functions, reducing the need for manual intervention. This leads to cost savings by lowering the labor required for these tasks and enabling businesses to make more informed decisions in real time.
Enhancing Scalability and Flexibility
On-Demand Resources
The cloud offers organizations the ability to scale resources up or down on demand, which is particularly valuable for businesses with fluctuating workloads or seasonal demands. Instead of overcommitting to fixed IT resources or infrastructure, companies can adjust their cloud resources to match their current needs. This level of flexibility reduces waste and ensures that businesses only pay for the resources they require at any given time.
For example, an e-commerce business experiencing a surge in traffic during the holiday season can easily scale its cloud infrastructure to handle the increased demand. Once the peak season is over, the company can scale down its resources, avoiding the costs associated with maintaining excess capacity.
Global Reach and Reduced Geographical Costs
Cloud services enable businesses to expand their operations globally without the need to establish physical offices or data centers in different regions. With cloud infrastructure, organizations can host their services in various regions and ensure that customers have access to fast, reliable services regardless of their geographic location. This global reach can save businesses significant costs associated with building and maintaining physical presence in multiple regions.
Conclusion
Migrating to the cloud offers numerous cost-saving advantages for businesses, from reducing capital expenditures to optimizing operational costs and enhancing scalability. By eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure, streamlining IT maintenance, and enabling businesses to scale resources on-demand, cloud migration provides a cost-efficient solution that aligns with the modern business landscape.
As organizations continue to adopt cloud solutions, they can not only reduce their overall costs but also improve efficiency, increase productivity, and gain greater flexibility. However, it’s important for businesses to carefully assess their cloud migration strategy to ensure they are selecting the right cloud services, optimizing usage, and taking full advantage of the cloud’s capabilities.
Ultimately, cloud migration is a powerful tool for businesses looking to remain competitive in an increasingly digital world while reducing costs and driving innovation.